Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Key Laboratory for Biomedical Measurements and Ultrasound Imaging, National-Regional Key Technology Engineering Laboratory for Medical Ultrasound, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen University Medical School, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
3 College of Physics and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
4 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson SC 29634, US
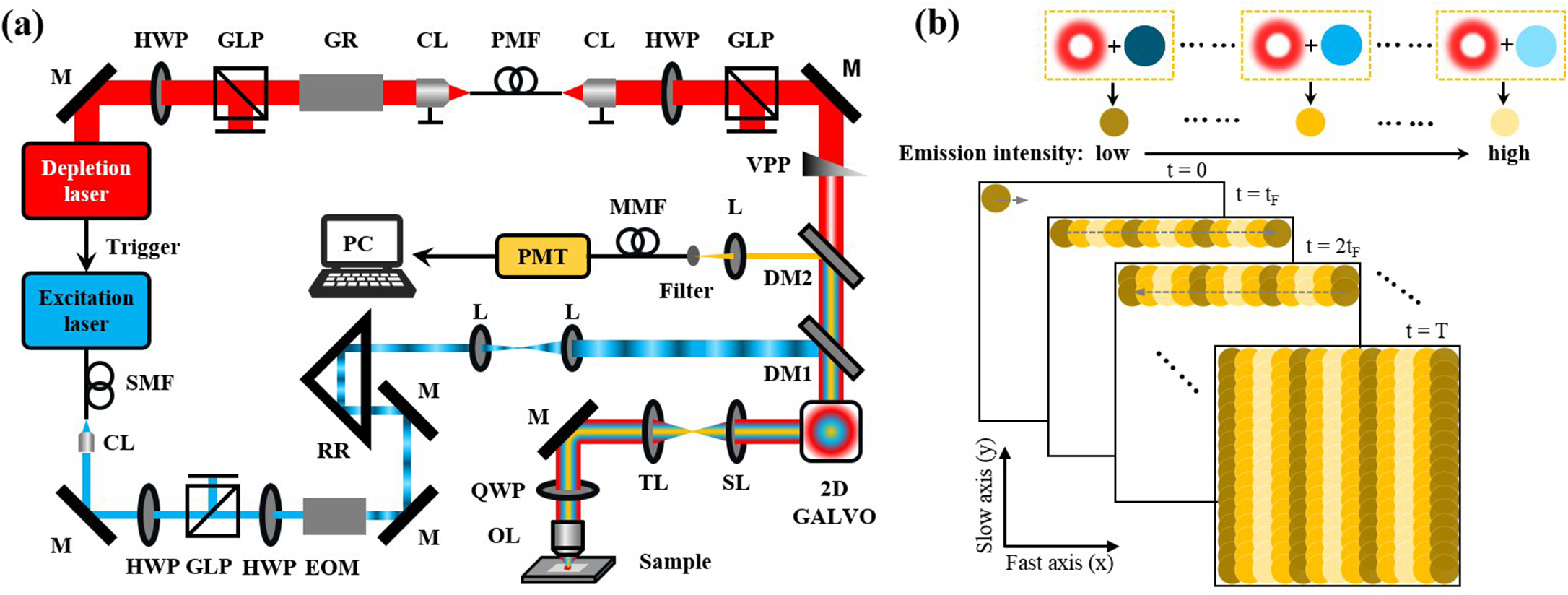
Wide-field linear structured illumination microscopy (LSIM) extends resolution beyond the diffraction limit by moving unresolvable high-frequency information into the passband of the microscopy in the form of moiré fringes. However, due to the diffraction limit, the spatial frequency of the structured illumination pattern cannot be larger than the microscopy cutoff frequency, which results in a twofold resolution improvement over wide-field microscopes. This Letter presents a novel approach in point-scanning LSIM, aimed at achieving higher-resolution improvement by combining stimulated emission depletion (STED) with point-scanning structured illumination microscopy (psSIM) (STED-psSIM). The according structured illumination pattern whose frequency exceeds the microscopy cutoff frequency is produced by scanning the focus of the sinusoidally modulated excitation beam of STED microscopy. The experimental results showed a 1.58-fold resolution improvement over conventional STED microscopy with the same depletion laser power.
stimulated emission depletion structured illumination microscopy superresolution microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, Guangdong, P. R. China
2 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson, SC 29634 USA
Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) is suitable for biological samples because of its relatively low-peak illumination intensity requirement and high imaging speed. The system resolution is affected by two typical detection modes: Point detection and area detection. However, a systematic analysis of the imaging performance of the different detection modes of the system has rarely been conducted. In this study, we compared laser point scanning point detection (PS-PD) and point scanning area detection (PS-AD) imaging in nonconfocal microscopy through theoretical analysis and simulated imaging. The results revealed that the imaging resolutions of PS-PD and PS-AD depend on excitation and emission point spread functions (PSFs), respectively. Especially, we combined the second harmonic generation (SHG) of point detection (P-SHG) and area detection (A-SHG) with SIM to realize a nonlinear SIM-imaging technique that improves the imaging resolution. Moreover, we analytically and experimentally compared the nonlinear SIM performance of P-SHG with that of A-SHG.
Super-resolution structured illumination microscopy second harmonic generation Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2023, 16(4): 2350010
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,射频异质异构集成全国重点研究实验室,光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
面向生物粒子操控方法的研究,在生物医学和生命科学等领域具有重要意义。光镊操控具有无接触与高精度的特点,已被广泛应用于多个领域的研究中。然而,传统光镊的光热效应以及衍射极限都制约着光镊在生物医学领域的更广泛应用和发展。近十年来,研究者们将光热效应化劣势为优势,利用光与热的耦合效应实现了多种粒子的精确捕获及操控,即光致温度场光镊(OTFT)。由于此种新型光镊对光能的利用率极高,能量密度低于传统光镊近3个数量级,并可实现颗粒的大范围操控,极大地拓展了光镊可操控粒子的种类,已经成为纳米技术以及生命科学领域的重要研究工具。温度场光镊仍面临诸多问题,例如对于颗粒界面调控的依赖性以及三维捕获受限等,尤其是在生物光子学的研究中,还需要进一步发展和优化。本文对光致温度场光镊操控基本原理及其在生物医学中的应用两个方面进行了系统阐述,并对其今后的发展与挑战进行了展望。
光镊 光热镊 光流控 光热效应 微流控 生物传感器 光学学报
2023, 43(14): 1400001
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院, 光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
二次谐波产生(SHG)成像技术是一种针对非中心对称生物组织的免标记成像技术,已经成为生命科学研究的重要手段。衍射极限使得SHG技术无法分辨衍射极限以下的精细结构。虽然超分辨显微技术取得了突破性进展,但是SHG的相干非线性过程限制了SHG超分辨显微技术的发展。提出了一种点扫描结构光照明SHG超分辨显微(SHG-psSIM)技术,实现了氧化锌颗粒和小鼠尾腱的超分辨SHG显微成像。在传统的SHG显微系统的激发光路中引入电光调制器,通过对激发光正弦调制产生点扫描结构照明图案。基于点扫描结构照明图案与样本结构相互作用产生的莫尔条纹效应,将原本不可探测的样本高频信息搬移到显微镜通频带内,并利用光电倍增管探测。最后,利用软件重构出超分辨率图像。对比传统SHG系统,SHG-psSIM分辨率提高了1.86倍。
显微 二次谐波产生 二次谐波产生显微 结构光照明显微 超分辨显微 光学学报
2022, 42(10): 1018001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson, SC 29634, USA
Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) is an essential super-resolution microscopy technique that enhances resolution. Several images are required to reconstruct a super-resolution image. However, linear SIM resolution enhancement can only increase the spatial resolution of microscopy by a factor of two at most because the frequency of the structured illumination pattern is limited by the cutoff frequency of the excitation point spread function. The frequency of the pattern generated by the nonlinear response in samples is not limited; therefore, nonlinear SIM (NL-SIM), in theory, has no inherent limit to the resolution. In the present study, we describe a two-photon nonlinear SIM (2P-SIM) technique using a multiple harmonics scanning pattern that employs a composite structured illumination pattern, which can produce a higher order harmonic pattern based on the fluorescence nonlinear response in a 2P process. The theoretical models of super-resolution imaging were established through our simulation, which describes the working mechanism of the multi-frequency structure of the nonsinusoidal function to improve the resolution. The simulation results predict that a 5-fold improvement in resolution in the 2P-SIM is possible.
Super-resolution image structured illumination microscopy nonsinusoidal function Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2021, 14(5): 2142002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optoelectronics Engineering Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, P. R. China
2 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson, SC 29634, USA
Using the combination of a reflective blazed grating and a reflective phase-only diffractive spatial light modulator (SLM), scanless multitarget-matching multiphoton excitation fluorescence microscopy (SMTM-MPM) was achieved. The SLM shaped an incoming mode-locked, near-infrared Ti:sapphire laser beam into an excitation pattern with addressable shapes and sizes that matched the samples of interest in the field of view. Temporal and spatial focusing were simultaneously realized by combining an objective lens and a blazed grating. The fluorescence signal from illuminated areas was recorded by a two-dimensional sCMOS camera. Compared with a conventional temporal focusing multiphoton microscope, our microscope achieved effective use of the laser power and decreased photodamage with higher axial resolution.
Multitarget-matching multiphoton microscopy SLM temporal focusing Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2018, 11(2): 1750013
1 深圳大学光电工程学院光电子器件与系统(教育部/广东省)重点实验室深圳市传感器技术重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
2 深圳市进出口检验检疫局, 广东 深圳 350007
3 福建师范大学医学光电科学与技术教育部重点实验室福建省光子技术重点实验室, 福建 福州 350007
本文提出了基于光谱扫描技术的非机械扫描的表面等离子体共振(SPR)传感技术,采用白光为SPR激发光源,通过单色仪控制入射光的波长实现光谱寻址,在保证灵敏度和动态范围的同时,使系统在整个动态范围内具有较好的线性,简化了传感器结构.理论分析了光谱扫描SPR传感技术的灵敏度和动态范围,搭建了实验系统,并测量了不同浓度的酒精水混合溶液的SPR信号变化.结果表明:系统折射率测量范围为1.30-1.38,灵敏度可达3.1×105RIU.
表面等离子体共振 表面等离子体共振成像 传感器 波长寻址 SPR SPR imaging sensor wavelength addressing
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen 518060, P. R. China
2 School of Technical Physics, Xidian University Xi'an 710071, P. R. China
3 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET Clemson University, Clemson SC 29634, USA
Multifocal multiphoton microscopy (MMM) has recently become an important tool in biomedicine for performing three-dimensional fast fluorescence imaging. Using various beamsplitting techniques, MMM splits the near-infrared laser beam into multiple beamlets and produces a multifocal array on the sample for parallel multiphoton excitation and then records fluorescence signal from all foci simultaneously with an area array detector, which significantly improves the imaging speed of multiphoton microscopy and allows for high efficiency in use of the excitation light. In this paper, we discuss the features of several MMM setups using different beamsplitting devices, including a Nipkow spinning disk, a microlens array, a set of beamsplitting mirrors, or a diffractive optical element (DOE). In particular, we present our recent work on the development of an MMM using a spatial light modulator (SLM).
Multifocal multiphoton microscopy (MMM) microlens array beamsplitter diffractive optical element (DOE) spatial light modulator (SLM) Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2012, 5(3): 1250018
深圳大学光电工程学院, 光电子器件与系统(教育部, 广东省)重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
在荧光显微镜中,微弱的荧光信号一般淹没于较强的激发光中,显微镜的成像质量在很大程度上取决于提取微弱荧光信号的能力。目前,荧光显微镜均根据荧光与激发光波长的差异,采用频率滤波法滤除激发光,实现图像增强。但该方法不仅对滤光片要求高,而且对荧光和激发光的波长有严重的依赖性。基于激发光与荧光在偏振态上的差异,提出了一种用于荧光显微镜的正交偏振滤波图像增强技术。研究表明,正交偏振滤波图像增强技术能够显著地提高成像质量,对光学元件性能参数的要求大幅度降低。丰富了从强激发光中提取弱荧光信号的技术手段,为今后解决波长可调谐的多光谱荧光显微镜、白光照明多光谱荧光显微镜等技术上的瓶颈提供了参考。
生物光学 荧光显微镜 图像增强 正交偏振 滤波 中国激光
2012, 39(10): 1004002
1 海军潜艇学院防化教研室, 山东 青岛 266042
2 深圳大学光电工程学院光电子器件与系统(教育部/广东省)重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
3 克莱姆森大学生物工程学系, 美国南卡莱罗纳州克莱姆森 29634
发展了一种新型的多焦点多光子激发荧光显微技术,通过软件控制空间光调制器,在所需要的成像区域产生相应的激发光点阵,通过扫描入射角实现激发点阵快速并行扫描激发,通过CCD并行记录所产生的荧光信号,获得任意视场图像。分别实现了10×10和50×50点阵激发下的全视场双光子荧光图像,并且实现了同时多个区域寻址的多焦点激发成像。对比其他多焦点显微技术,该技术具有明显的灵活性,不但保持了多焦点激发的快速成像的优点,而且还增加了任意数量成像区域同时寻址和阵列点密度变化,所有这些变化只需要通过软件加载相应的相位图案给空间光调制器,而不需要任何硬件更改。
显微 多焦点 多光子 空间光调制器 光学学报
2012, 32(10): 1018001





